
Apollo and Luna Reflectors
Jump to: Mission Objectives, Mission Instrumentation, Mission Parameters, Additional Information
Mission Photos:
 |
 |
Mission Objectives:
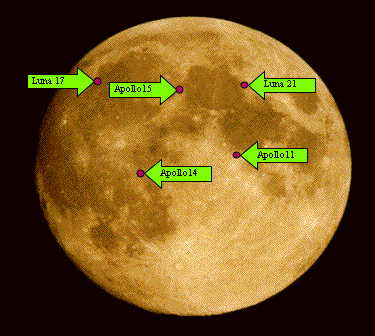
In July 1969, Apollo 11 astronauts Neil Armstrong and Buzz Aldrin deployed a variety of scientific experiments in the fine powder of Mare Tranquillitatis (0.6734° N, 23.473° E). Among those devices was a laser ranging retroreflector, which, more than 50 years later, still yields fundamental scientific data. Other retroreflectors have since been placed on the Moon [Bender et al., 1973]. The second lunar laser retroreflector was carried on the Lunokhod 1 rover in 1970 by the Luna 17 mission and is located in Mare Imbrium (38.3152° N, 35.0080° W). In January and July 1971 respectively, the Apollo 14 and 15 missions deployed lunar laser retroreflectors to the Fra Mauro formation (3.6442° S, 17.4786° W) and to Hadley Rille (26.1334° N, 3.6285° E). Finally in 1973, the Luna 21 mission deployed the Lunokhod 2 rover carrying a lunar laser retroreflector. The Luna 21 retroreflector is located in Le Monnier crater on the eastern edge of Mare Serenitatis (25.8323° N, 30.9221° E). The Luna 17 retroreflector initially lacked a precise position and was unavailable to LLR until the rover was located in images provided by NASA’s Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter [Murphy et al., 2011].
Lunar Laser Ranging (LLR) operates with the same principle as Satellite Laser Ranging (SLR) to Earth orbiting satellites: Short pulses of laser light are directed at a retroreflector target where they bounce back to the station. The station measures the departure and arrival times with high precision, allowing a precise computation of the round-trip range between the tracking station and the target. The challenge associated with LLR is the large distance (∼357,000 to 407,000 km) to the target and a signal strength that depends on the inverse fourth power of that distance. Thus, the signal return from LLR is about 107 times weaker than from a similar reflector placed at the LAGEOS-1 altitude. Therefore, only a few terrestrial stations have the technical capability to carry out two-way (round-trip) Lunar Laser Ranging (LLR) [Müller et al., 2019].
The terrestrial laser ranging stations that have performed LLR have included the McDonald Observatory, Texas (1969–2013) [e.g., Shelus et al., 1996; Shelus 1986], the Crimean Astrophysical Observatory (1974; 1982-1984) [Tryapitsyn et al., 2021; Yagudina et al., 2018], the Côte d’Azur Observatory, Grasse, France (1984–present) [Chabé et al., 2020a; Samain et al., 1998], the Haleakala Observatory, Maui, Hawaii (1984-1990), the Matera Laser Ranging Observatory (MLRO), Italy (2003–present), the Apache Point Observatory (APOLLO), New Mexico, (2006 – present) [Battat et al., 2023; Colmenares et al., 2022; Adelberger et al., 2017; Murphy et al., 2008], and the Geodetic Observatory Wettzell, Germany [Eckl, 2023; Eckl et al., 2019]. Other terrestrial stations that have also demonstrated LLR include Kunming, China [Yuqiang et al., 2019] and the TianQin Laser Ranging station, Zhuhai, China [Zhang et al., 2022].
LLR data are able to determine many parameters associated with the dynamics of the Earth-Moon system, including tidal dissipation and the rate of recession of the Moon from the Earth, the lunar ephemeris, lunar physics, the structure and state of the Moon’s interior, reference frames, and Earth orientation parameters. LLR data have been used to provide powerful tests of general relativity. They have also been used to solve for parameters related to gravitational physics, such as the temporal variation of the gravitational constant (G), as well as tests for the equivalence principle [e.g., Chabé et al, 2020b; Müller et al., 2019; Hofmann and Müller, 2018; Williams et al., 2016; Pavlov et al., 2016; Williams et al., 2012; Dickey et al., 1994].
Mission Instrumentation:
The only instrumentation on the moon related to laser ranging are the five retro-reflectors arrays (three US, two French/Soviet).
Mission Parameters:
| Lunar Parameters | |||||
| Apollo 11 | Luna 17 | Apollo 14 | Apollo 15 | Luna 21 | |
| Sponsor: | United States | U.S.S.R. and France | United States | United States | U.S.S.R and France |
| Life: | Many decades | Many decades | Many decades | Many decades | Many decades |
| Applications: | Lunar science | Lunar science | Lunar science | Lunar science | Lunar science |
| COSPAR ID: | 0000100 | 0000101 | 0000102 | 0000103 | 0000104 |
| Date: | Jul 21, 1969 | Nov 1, 1970 | Feb 5, 1971 | Jul 31, 1971 | Jan 15, 1973 |
| RRA Size: | 46 cm by 46 cm | 44 cm by 19 cm | 46 cm by 46 cm | 104 cm by 61 cm | 44 cm by 19 cm |
| RRA Shape: | Square | Rectangular | Square | Rectangular | Rectangular |
| Reflectors: | 100 | 14 | 100 | 300 | 14 |
| Orbit: | Elliptical | Elliptical | Elliptical | Elliptical | Elliptical |
| Inclination: | 5.145 degrees | 5.145 degrees | 5.145 degrees | 5.145 degrees | 5.145 degrees |
| Eccentricity: | 0.0549 | 0.0549 | 0.0549 | 0.0549 | 0.0549 |
| Perigee: | 356,400 km | 356,400 km | 356,400 km | 356,400 km | 356,400 km |
| Period: | 29.53 days | 29.53 days | 29.53 days | 29.53 days | 29.53 days |
Additional Information:
- CNRS Press Release, May 3, 2023. “The Moon’s heart revealed for the first time (La Lune ouvre son Coeur pour la première fois)”: (in English: https://www.cnrs.fr/en/press/moons-heart-revealed-first-time in French: https://www.cnrs.fr/fr/presse/la-lune-ouvre-son-coeur-pour-la-premiere-fois)
- NASA Press Release, Feb 4, 2021. “50 years ago: Apollo 14 Lands at Fra Mauro”: URL: https://www.nasa.gov/history/50-years-ago-apollo-14-lands-at-fra-mauro/
- NASA Press Release, Aug. 10, 2020. “Laser Beams Reflected Between Earth and Moon Boost Science”: URL: https://www.nasa.gov/missions/laser-beams-reflected-between-earth-and-moon-boost-science/
- NASA Press Release, July 24, 2019 (50th anniversary of LLR). “The Apollo Experiment that Keeps on Giving”: URL: https://www.nasa.gov/solar-system/the-apollo-experiment-that-keeps-on-giving/
- CNRS Press Release, July 9, 2019. “New estimate of the size of the lunar core from LLR (Nouvelle estimation de la taille du noyau de la Lune grâce aux mesures laser-lune”). (URL: https://www.cnrs.fr/fr/presse/nouvelle-estimation-de-la-taille-du-noyau-de-la-lune-grace-aux-mesures-laser-lune)
- NASA Press Release, Nov. 19, 2018. “50 years ago, On the way to the Moon: Lunar science announced”. URL: https://www.nasa.gov/history/50-years-ago-on-the-way-to-the-moon-lunar-science-announced/
- NIST (National Institute of Standards and Technology) Time Capsule, Sept. 26, 2017. “To the Moon and Back … in 2.5 seconds”. (URL: https://www.nist.gov/nist-time-capsule/any-object-any-need-call-nist/moon-and-back-25-seconds)
- Press Release, University of California, San Diego, Apr. 27, 2010: “Lost Reflector found on the Moon”. URL: https://phys.org/news/2010-04-lost-reflector-moon.html
- Press Release, SPIE, The international society for optics and photonics, Dec. 11, 2009. “Lunar laser ranging: 40 years of high-level science”. (URL: https://spie.org/news/12-09-laser-ranging)
- Luna 21/Lunokhod 2 (NASA Space Science Data Coordinated Archive) (URL: https://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraft/display.action?id=1973-001A)
- Luna 17/Lunokhod 1 (NASA Space Science Data Coordinated Archive) (URL: https://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraft/display.action?id=1970-095A)
- Apollo information from the Lunar and Planetary Institute (Apollo 11, Apollo 14, Apollo 15)
References:
- Adelberger E.G., Battat J.B.R., Birkmeier K.J., et al. (2017). “An absolute calibration system for millimeter-accuracy APOLLO measurements”, Classical & Quantum Gravity, 34(24), 245008, doi:10.1088/1361-6382/aa953b
- Battat J.B.R., Adelberger E., Colmenares N.R. et al. (2023). “Fifteen years of millimeter accuracy lunar laser ranging with APOLLO: Data set characterization”, Pub. Astron. Soc. Pacific, 135(1052), doi: 10.1088/1538-3873/aceb2f
- Bender, P., Currie, D.G., Dicke, R.H., Eckhardt, D.H., Faller, J.E., et al, "The Lunar Laser Ranging Experiment", Science, 182, 4109, 229-238, doi: 10.1126/science.182.4109.22
- Chabé J., Courde C., Torre J.-M. et al. (2020a). “Recent progress in lunar laser ranging at Grasse laser ranging station”, Earth and Space Science. 7, e2019EA000785. doi:10.1029/2019EA000785
- Chabé J., Bourgoin A., Rambaux N. (2020b). “Histoire de la télémétrie laser terre-lune”, Photoniques, 103, 26–29, doi: 10.1051/photon/202010326
- Colmenares N.R., Battat J.B.R., Gonzales D.P. et al. (2022). “Recent developments at the Apache Point Lunar Laser Ranging Station”, Proceedings of the 22nd International Laser Ranging Workshop, Yebes, Spain, Nov. 7–11, 2022, (URL: https://ilrs.gsfc.nasa.gov/lw22/presentations/S10/S10-O01_Colmenares.pdf)
- Dickey J.O., Bender P.L., Faller J.E. et al. (1994).”Lunar laser ranging – A continuing legacy of the Apollo program”, Science, 265(5171), 482–490, doi: 10.1126/science.265.5171.482
- Eckl, J. (2023). “Lunar laser ranging at the WLRS”, Presentation at the ILRS Lunar Laser Ranging Meeting, Grasse, France, September 14–15, 2023. (Presentation)
- Eckl J.J., Schreiber K.U., Leidig, A., Bachem T., Neidhardt A., Schüler T. (2019). “Lunar Laser Ranging: A small system approach”, Abstract G31B-647, 2019 Fall Meeting of the American Geophysical Union, San Francisco, California, U.S.A., 9–13 December 2019. (Abstract: https://agu.confex.com/agu/fm19/meetingapp.cgi/Paper/503572). (Presentation)
- Hofmann F. and Müller J. (2018). “Relativistic tests with lunar laser ranging”, Classical and Quantum Gravity, 35(3), doi: 10.1088/1361-6382/aa8f7a
- Müller J., Murphy T.W., Schreiber U. et al. (2019). “Lunar Laser Ranging: a tool for general relativity, lunar geophysics, and Earth science”, J. Geodesy, 93, 2195–2210, doi: 10.1007/s00190-019-01296-0
- Murphy T.W., Adelberger E.G, Battat J.B.R., et al. (2008). “The Apache point observatory lunar laser-ranging operation: instrument description and first detections”, Publ Astron Soc Pac, 120, 20–37, doi:10.1086/526428
- Murphy T.W., Adelberger E.G., Battat J.B.R., et al. (2011). “Laser ranging to the lost Lunokhod 1 reflector”, Icarus 211:1103–1108, doi: 10.1016/j.icarus.2010.11.010
- Pavlov D.A., Williams J.G., Suvorkin V.V. (2016). “Determining parameters of Moon’s orbital and rotational motion from LLR observations using GRAIL and IERS-recommended models’, Cel. Mech. And Dyn. Astron., 126(1-3), 61–88, doi: 10.1007/s10569-016-9712-1
- Samain E., Mangin J.F., Veillet C. et al. (1998). “Millimetric Lunar Laser Ranging at OCA (Observatoire de la Côte d’Azur)”, Astron. Astrophys. Suppl. Ser. 130, 235–244, doi: 10.1051/aas:1998227
- Schreiber U., Müller J., Reiner D. et al. (1993). “LLR: Activities at Wettzell”, Proceeedings of the 8th International Workshop on Laser Ranging”, Annapolis, Maryland, U.S.A., May 18-22, 1992, URL: https://ntrs.nasa.gov/citations/19940011127
- Shelus P.J. (1985). “MLRS: a lunar/artificial satellite laser ranging facilityvat the McDonald observatory”, IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens, 23, 385–390, doi:10.1109/TGRS.1985.289428
- Shelus P.J., Ricklefs R.L., Ries J.G., Whipple A.L., Wiant J.R. (1996). “McDonald observatory lunar laser ranging: Beginning the second 25 years”, 172nd Symposium of the International Astronomical Union on Dynamics, Ephemerides and Astrometry of the Solar System , 172:409-414. doi:10.1017/S0074180900127755
- Tryapitsyn V.N., Pavlov D.A., Rumyantsev V.V. (2021). “The 1970-1984 lunar laser ranging observations at the Crimean Astrophysical Observatory”, Journal for the History of Astronomy, 52(1), doi: 10.1177/002182862198911
- Williams J.G., Turyshev S.G., Boggs D.H. (2012). “Lunar laser ranging tests of the equivalence principle”, Classical and Quantum Gravity, 29(18), doi: 10.1088/0264-9381/29/18/184004
- Williams J.G., Boggs D.H. (2016). “Secular tidal changes in lunar orbit and Earth rotation”, Cel. Mech. And Dyn. Astron., 126(1-3), 89–129, doi: 10.1007/s10569-016-9702-3
- Yagudina E.I., Pavlov D.A., Tryapitsyn V.N., Rumyantsev V.V. (2018). “Processing and analysis of lunar laser ranging observations in Crimea in 1974–1984”, Proceedings of the 21st International Workshop in Laser Ranging, Canberra, Australia, Nov. 4-9, 2018. [URL: https://ilrs.gsfc.nasa.gov/lw21/docs/2018/papers/B30_Ignatenko_paper.pdf]
- Yuqiang L., Rongwang L., Zhulian L. et al. (2019). “Lunar Laser Ranging Research and Experiment in Yunnan Observatories”, Proceedings of the 2019 ILRS Technical Workshop, Stuttgart, Germany, Oct. 21–25, 2019. URL: https://ilrs.gsfc.nasa.gov/2019_Technical_Workshop/docs/2019/abstracts/session2_Li_abstract.pdf
- Zhang C., Gao T., Cao Y. et al. (2022). “The facilities and performance of TianQin laser ranging station”, Classical and Quantum Gravity, 39(12), doi: 10.1088/1361-6382/ac6d3e
Historical Publications:
- Alley, C.O., Bowman, S.R., Rayner, J.D., Wang, B.C., and Yang, F.M., "First Lunar Ranging Results from The University of Maryland Research Station at the 1.2M Telescope of the GSFC," Proc. of the 6th International Workshop on Laser Ranging Instrumentation, Antibes, France, September 22-26, p. 625, 1986.
- Bender, P.L., Faller, J.E., Hall, J.L., Degnan, J.J., Dickey, J.O., Newhal, X X, Williams, J.G., King, R.W., Machnik, L.O., O'Gara, D., Ricklefs, R.L., Shelus, P.J., Whipple, A.L., Wiant, J.R. and Veillet, C., "Microwave and Optical Lunar Transponders", Astrophysics from the Moon, AIP Conf. Proc. Series, (American Institute of Physics New York), pp. 647-653, April, 1990.
- Bourdet, H. and Dumoulin, C., "Description of the 1.5 in Telescope Realized by INAG for the CERGA Lunar Laser Ranging System", Proc. of the 4th International Workshop on Laser Ranging Instrumentation, Austin, Texas, published by Geodetic Institute, Univ. of Bonn, October 12-16, p. 190, 1981.
- Bowman, S.R., Alley, C.O., Degnan, J.J., Cao, W.L., Zhang, M.Z. and Wang, N.H., "New Laser Developments Toward a Centimeter Accuracy Lunar Ranging System", 5th International Workshop on Laser ranging Instrumentation, Herstmonceux, U.K., published by Geodetic Institute, Univ. Bonn, p. 480, 1984.
- Bowman, S.R., Rayner, J.R. and Alley, C.O., "Analysis and Performance of a Passive Polarization Telescope Coupling Switch For Lunar Laser Ranging", Proc. of the 6th International Workshop on Laser Ranging Instrumentation, Antibes, France, September 22-26, p. 273, 1986.
- Calame, O. and Gaignebet, J., "French Lunar Laser Ranging Station", Proc. of the 3rd International Workshop on Laser Ranging Instrumentation, Lagonissi, Greece, May 23-27, p. 139, 1978.
- Chapront, J., Chapront-Touze, M. and Francou, G., "A new determination of lunar orbital parameters, precession constant and tidal acceleration from LLR measurements", Astronomy and Astrophysics. Vol. 387, p. 700, 2002.
- Charlot, P., Sovers, O.J., Williams, J.G. and Newhall, X X, "Precession and nutation from joint analysis of radio interferometric and lunar laser ranging observations", Astron. J., 109, pp. 418-427, 1995.
- Davies, M.E., Colvin, T.R. and Meyer, D.L., "A Unified Lunar Control Network: The Near Side", J. Geophys. Res., 92, pp. 14177-14184, 1987.
- Dickey, J.O., Williams, J.G., and Eubanks, T.M., "Earth Rotation and Polar Motion: Results from Lunar Laser Ranging Analysis and an Intercomparison Study", Proc. of the IAG, V.2, 18th Gen. Assembly, Hamburg, pp. 12-27, 1983
- Dickey, J.O., Williams, J.G., and Newhall, X X, "Fifteen Years of Lunar Laser Ranging Accomplishments and Future Challenges", 5th International Workshop on Laser ranging Instrumentation, Herstmonceux, U.K., published by Geodetic Institute, Univ. Bonn, p. 19, 1984.
- Dickey, J., "Lunar Geophysics, Geodesy, and Dynamics (Invited)", Presentation to 13th International Workshop on Laser Ranging, Washington, DC, USA, October 7-11, 2002.
- Faller, J.E., Bender, P.L., Alley, C.O., Currie, D.G., and 7 others, "Geodesy Results Obtainable with Lunar Retroreflectors", The Use of Artificial Satellites for Geodesy, AGU, pp. 261-264, 1972.
- Feng, H., Xiong, Y., Zhang, Y., and Wang, J., "An Accurate Test of the Azimuth Axis of a 1.2M Alt-AZ Telescope Mount for the Lunar Laser Ranging and the Analysis of the Results", Proc. of the 6th International Workshop on Laser Ranging Instrumentation, Antibes, France, September 22-26, p. 281, 1986.
- Folkner, W.M., Charlot, P., Finger, M.H., Williams, J.G., Sovers, O.J., Newhall, X X, and Standish, E.M.,"Determination of the extragalactic-planetary frame tie from joint analysis of radio interferometric and lunar laser ranging measurements", Astron. Astrophys. 287, 279-289, 1994.
- Gaignebet, J., "New Developments on Laser Transmitters for the GRGS/CERGA Satellite and Lunar Ranging Systems", Proc. of the 3rd International Workshop on Laser Ranging Instrumentation, Lagonissi, Greece, May 23-27, p. 220, 1978.
- Gaignebet, J., and Sinet, C., "TV Guiding for Satellite and Lunar Ranging", Proc. of the 3rd International Workshop on Laser Ranging Instrumentation, Lagonissi, Greece, May 23-27, p. 208, 1978.
- Greene, B., C. Smith, Y. Gao, J. Cotter, C. Moore, J. Luck, I. Ritchie, "Lunar Ranging from Mount Stromlo", 14th International Laser Ranging Workshop, San Fernando, Spain, June 7 - 11, 2004.
- Huang, C., Jin, W., and Xu, H., "Adaptive Ridge Regression. the Multicollinearity and its Remedy- a Case in Lunar Laser Ranging", Proc. of the 10th International Workshop on Laser Ranging Instrumentation, Shanghai Observatory, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai, China, November 11-15, p. 168, 1996.
- Kiernan, E., and White, M.L., "A Description of the Mt. Haleakala Satellite and Lunar Laser Ranging Software", 5th International Workshop on Laser ranging Instrumentation, Herstmonceux, U.K., published by Geodetic Institute, Univ. Bonn, p. 371, 1984.
- Kokurin, Yu. L., Kurbasov, V.V., Lobanov, V.F., and Sukhanovsky, A.N., "Crimean Lunar Laser Ranging System", Proc. of the 2nd International Workshop on Laser Ranging Instrumentation, Prague, Czechoslovakia, August 11- 16, p. 39, 1975.
- Kokurin, Yu. L., Kurbasov, V.V., Lobanov, V.F., and Sukhanovsky, A.N., "Crimean Lunar Laser Ranging System", Proc. of the 3rd International Workshop on Laser Ranging Instrumentation, Lagonissi, Greece, May 23-27, p. 143, 1978.
- Konopliv, A.S., Binder, A.B., Hood, L.L., Kucinskas, A.B., Sjogren, W.L., and Williams, J.G., "Improved gravity field of the Moon from Lunar Prospector", Science 281, 1476-1480, 1998.
- Larden, D.R., "Monitoring the Earth's Rotation by Lunar Laser Ranging", Univ. of New South Wales Rpt. No. S-20, 280pp, 1982.
- Larden, D.R., "The Likely Impact of Tectonic Plate Motion on Earth Rotation Results from Lunar Laser Ranging", Manuscriptica Geodetica,9, pp. 137-15, 1984.
- Leick, A., "Earth Orientation from Lunar Laser Range Differencing", OSU-Rpt. 263, 110pp, 1978.
- Mangin, J.F., "The Laser and the Calibration of the CERGA Lunar Ranging System", Proc. of the 4th International Workshop on Laser Ranging Instrumentation, Austin, Texas, published by Geodetic Institute, Univ. of Bonn, October 12-16, p. 313, 1981.
- Mangin, J.F., Chabaudie, J.E., Feraudy, D., Fridelance, P., Furia, M., Glentzlin, M., Journet, A., Pham Van, J., Samain, E., Torre, J.M., and Vigouroux, G., "Millimetric Lunar Laser Ranging O.C.A/C.E.R.G.A", Proc. of the 10th International Workshop on Laser Ranging Instrumentation, Shanghai Observatory, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai, China, November 11-15, p. 189, 1996.
- Mangin, J.F., Chapront, J., and teams, "New Improvements in the Reduction of LLR Observations, News of the LLR Grasse with a particular night of Full Moon", Presentation to 12th International Workshop on Laser Ranging, Matera, Italy, November 13-17, 2000.
- Mangin, J.F., Dumoulin, Ch., Torre, J.M., Sagnier, J.L., Kovalevsky, J., and Feraudy, D., "Description and First Results of the CERGA Lunar Laser Station", Proc. of the 4th International Workshop on Laser Ranging Instrumentation, Austin, Texas, published by Geodetic Institute, Univ. of Bonn, October 12-16, p. 291, 1981.
- Michael, W.H., and Tolson, R.H., "The Lunar Orbiter Project Selenodesy Experiment", The Use of Artificial Satellites for Geodesy Vol. II, pp. 609-634, 1967.
- Morgan, P., "A Schematic of the Australian Lunar Ranger", Proc. of the 2nd International Workshop on Laser Ranging Instrumentation, Prague, Czechoslovakia, August 11- 16, p. 89, 1975.
- Morgan, P.J., and King, R.V., "The M.I.T. Lunar and Planetary Ephemeris", Proc. of the 4th International Workshop on Laser Ranging Instrumentation, Austin, Texas, published by Geodetic Institute, Univ. of Bonn, October 12-16, p. 239, 1981.
- Mulholland, J.D., and Calame, O., "Scientific Goals of Lunar Laser Ranging", Proc. of the 3rd International Workshop on Laser Ranging Instrumentation, Lagonissi, Greece, May 23-27, p. 22, 1978.
- Murphy, T., "The Apache Point Observatory Lunar Laser-ranging Operation (APOLLO)", Presentation to 12th International Workshop on Laser Ranging, Matera, Italy, November 13-17, 2000.
- Murphy, T., "APOLLO: Multiplexed Lunar Laser Ranging", Presentation to 13th International Workshop on Laser Ranging, Washington, DC, USA, October 7-11, 2002.
- Murphy, T., "The Apache Point Observatory Lunar Laser Ranging Operation (APOLLO)", 14th International Laser Ranging Workshop, San Fernando, Spain, June 7 - 11, 2004.
- Mueller, J., and Tesmer, V., "Investigation of Tidal Effects in Lunar Laser Ranging", Journal of Geodesy, Vol. 76, P. 232-237, 2002.
- Newhall, X X, Williams, J.G., and Dickey, J.O., "Earth Rotation (UT0-UTC and Variation of Latitude) from Lunar Laser Ranging", International Earth Rotation Service Note 17, ed. P. Charlot, M7-M12, 1994.
- Newhall, X X, Williams, J.G., and Dickey, J.O., "Earth Rotation (UT0) from Lunar Laser Ranging", JPL preprint No.175, submitted for the IERS annual report, 1989.
- Newhall, X X, Williams, J.G., and Dickey, J.O., "Earth Rotation (UT0R) from Lunar Laser Ranging", JPL Pre-print No.145, for submission to the BIH Annual Report, 1986.
- Newhall, X X, Williams, J.G., and Dickey, J.O., "Earth Rotation (UT0R) from Lunar Laser Ranging", JPL Pre-print No.157, 1987.
- Newhall, X X, Williams, J.G., and Dickey, J.O., "Earth Rotation (UT0R) from Lunar Laser Ranging", JPL Pre-print No.168, 1988.
- Newhall, X X, Williams, J.G., and Dickey, J.O., "Earth Rotation from Lunar Laser Ranging", JPL Pre-print No.153, 1986.
- Newhall, X X, Williams, J.G., and Standish, E.M., "Planetary and Lunar Ephemerides, Lunar Laser Ranging, and Lunar Physical Librations", in Dynamics, Ephemerides and Astrometry of the Solar System, eds. S. Ferraz-Mello, B. Morando, and J.-E. Arlot, 37-44, 1996.
- Newhall, X X, and Williams, J.G., "Estimation of the Lunar Physical Librations", Celestial Mech. and Dyn. Astron. 66, 21-30, 1997.
- Ries, J. Gyorgyey R.L. Ricklefs, P.J. Shelus, J.R. Wiant, "UT0 and Variation of Latitude Determination from Lunar Laser Ranging Observations for 1969-1998", 1998 IERS Annual Report, Observatoire de Paris, France, 1999.
- Ricklefs, R., "Consolidated Laser Ranging Prediction Format: Implications for Lunar Laser Ranging", 14th International Laser Ranging Workshop, San Fernando, Spain, June 7 - 11, 2004.
- Ricklefs, R.L., and Ries, J.G., "Lunar Laser Ranging Data Processing in a Unix X Windows Environment", Proc. 8th Intern. Workshop on Laser Ranging Instrumentation, Annapolis, MD, May 18-22, 1993, NASA Conference Publ. 3214, p. 10-6, 1992.
- Ries, J.G., Jefferys, W.H., and Shelus, P.J., "A Different Approach to Lunar Data Analysis: The Application of Bayesian Statistics", Proc. of the 11th International Workshop on Laser Ranging, Deggendorf, Germany, September 21-25, p. 223, 1998.
- Samain, E., G. Aridon, P. Exertier, J.F. Mangin, G.M. Lagarde, J.L. Oneto, J. Paris, F. Pierron, J.M. Torre, "MEO: The Future of the French Lunar Laser Ranging Station", 14th International Laser Ranging Workshop, San Fernando, Spain, June 7 - 11, 2004.
- Samain, E., and Mangin, J., "Detector Studies for Millimetric Lunar Laser Ranging at OCA", Proc. of the 9th International Workshop on Laser Ranging Instrumentation, Australian Government Publishing Service, Canberra, p . 449, 1994.
- Shelus, P., "Improved Lunar Science through better Observational Strategies", Presentation to 12th International Workshop on Laser Ranging, Matera, Italy, November 13-17, 2000.
- Shelus, P., Ricklefs, R., Ries, J., Whipple, A., Wiant, J., "Lunar Laser Ranging at McDonald Observatory: An Upgrade to Start the 2nd Quarter Century", Proc. of the 9th International Workshop on Laser Ranging Instrumentation, Australian Government Publishing Service, Canberra, p . 295, 1994.
- Shelus, P.J., "A Simple Software Scheduling Tool for Efficient Observing Operations At a Lunar /LAGEOS Laser Ranging Station", Proc. of the 6th International Workshop on Laser Ranging Instrumentation, Antibes, France, September 22-26, p. 511, 1986.
- Shelus, P.J., "MLRS: A Lunar/Artificial Satellite Laser Ranging Facility at the McDonald Observatory", IEEE Sat. Geodyn.-IEEE Trans. Geosci. and Rem. Sens., V.GE-23, pp. 385-390, 1985.
- Shelus, P.J., "The Science Derived from Lunar Laser Ranging", Proc. of the 10th International Workshop on Laser Ranging Instrumentation, Shanghai Observatory, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai, China, November 11-15, p. 2, 1996.
- Shelus, P.J., Ricklefs, R.L., Whipple, A.L., and Wiant, J.R., "Lunar Laser Ranging at McDonald Observatory: 1969 to the Present", Contributions of Space Geodesy in Geodynamics: Crustal Dynamics, AGU Geodynamics Series, V.25, pp. 183-188, Edited by D.E. Smith and D.L. Turcotte, 1993.
- Silverberg, E.C., "A Mobile Lunar Laser Station", Proc. of the 2nd International Workshop on Laser Ranging Instrumentation, Prague, Czechoslovakia, August 11- 16, p. 98, 1975.
- Silverberg, E.C., "Encouraging the Dual Purpose Station: Automated Lunar Guiding", Proc. of the 2nd International Workshop on Laser Ranging Instrumentation, Prague, Czechoslovakia, August 11- 16, p. 103, 1975.
- Silverberg, E.C., "The U.S. Lunar Laser Ranging Stations", Proc. of the 2nd International Workshop on Laser Ranging Instrumentation, Prague, Czechoslovakia, August 11- 16, p. 45, 1975.
- Silverberg, E.G., "Lunar Ranging Systems, Remarks by the Session Chairman", Proc. of the 3rd International Workshop on Laser Ranging Instrumentation, Lagonissi, Greece, May 23-27, p. 137, 1978.
- Sjogren, W., "Lunar Satellite Techniques Applicable to Earth Satellite Geodesy", The Use of Artificial Satellites for Geodesy and Geodynamics, pp. 449-468, 1974.
- Smith, D., M. Zuber, "Precision Orbit Determination of Low Altitude Lunar Spacecraft with Laser Systems", 14th International Laser Ranging Workshop, San Fernando, Spain, June 7 - 11, 2004.
- Tsuchiya, A., "Lunar and Satellite Ranging System at Tokyo Astronomical Observatory", Proc. of the 2nd International Workshop on Laser Ranging Instrumentation, Prague, Czechoslovakia, August 11- 16, p. 50, 1975.
- Veillet, C., Mangin, J.F., Chabaubie, J.E., Dumolin, C., Feraudy, D., and Torre, J.M., "Lunar Laser Ranging at CERGA for the Ruby Period (1981-1986)", Contributions of Space Geodesy in Geodynamics: Crustal Dynamics, AGU Geodynamics Series, V.25, pp. 189-194, 1993.
- Veillet, C., Mangin, J.F., and Torre, J.M., "First two colour ranging results at CERGA LLR station", Proc. of the 7th International Workshop on Laser Ranging Instrumentation, Matera, Italy October 2-8, published by OCA/CERGA, Grasse, France, p. 261, 1989.
- Veillet, C., and Torre, J., "Ranging the Moon with Two PC's", Proc. of the 9th International Workshop on Laser Ranging Instrumentation, Australian Government Publishing Service, Canberra, p . 300, 1994.
- Veillet, Ch., Bois, E., Chabaudie, J.E., Dumoulin, C., Feraudy, D., Glentzlin, M., Mangin, J.F., PhamVan, J., and Torre, J.M., "The CERGA lunar laser ranging station", Proc. of the 7th International Workshop on Laser Ranging Instrumentation, Matera, Italy October 2-8, published by OCA/CERGA, Grasse, France, p. 149, 1989.
- Veillet, Ch., Chabaudie, J.E., Dumoulin, Ch., Feraudy, D., Langlois, J.G., Mangin, J.F., Pham-Van, J., and Torre, J.M., "The New CERGA LLR Station", Proc. of the 6th International Workshop on Laser Ranging Instrumentation, Antibes, France, September 22-26, p. 129, 1986.
- VonBun, F.O., Kahn, W.D., Wells, W.T., and Conrad, T.D., "Determination of 5 x 5 Degree Gravity Anomalies Using Satellite-to-Satellite Tracking Between ATS-6 and Apollo", Geophys. J.R. Astron. Soc., 61, pp. 645-658, 1980.
- Wahr, J.M., and Larden, D.R., "An Analysis of Lunar Laser Ranging Data for the Earth's Free Core Nutation", the Proc. of the Ninth International Symp on Earth Tides, pp. 547-554, 1983.
- Williams, J.G., "Lunar And Planetary Ephemerides: Accuracy Inertial Frames and Zero Points", Proc. of the 4th International Workshop on Laser Ranging Instrumentation, Austin, Texas, published by Geodetic Institute, Univ. of Bonn, October 12-16, p. 309, 1981.
- Williams, J.G., Boggs, D.H., Dickey, J.O., and Folkner, W.M., "Lunar Laser Tests of Gravitational Physics", Marcel Grossmann IX, Rome, Italy, July 2-8, 2000, in Proc. of Ninth Marcel Grossmann Meeting (World Scientific Publ.), 2001.
- Williams, J. G., D. H. Boggs, J. O. Dickey, and W. M. Folkner, Lunar Laser tests of gravitational physics, in proceedings of The Ninth Marcel Grossmann Meeting, World Scientific Publ., eds. V. G. Gurzadyan, R. T. Jantzen, and R. Ruffini, 1797-1798, 2002.
- Williams, J.G., Boggs, D.H., Yoder, C.F., Ratcliff, J.T., and Dickey, J.O., "Lunar Dissipation in Solid Body and Fluid Core", Eos Transactions of the Amer. Geophys. Union 79, F546, 1998.
- Williams, J.G., Boggs, D.H., Yoder, C.F., Ratcliff, J.T., and Dickey, J.O., "Lunar Rotational Dissipation in Solid Body and Molten Core", submitted to J. Geophys. Res.-Planets, under revision, 2001.
- Williams, J., D. Boggs, S. Turyshev, J.T. Ratcliff, "Lunar Laser Ranging Science", 14th International Laser Ranging Workshop, San Fernando, Spain, June 7 - 11, 2004.
- Williams, J. G., and J. O. Dickey, Lunar Geophysics, Geodesy, and Dynamics, Proceedings of 13th International Workshop on Laser Ranging, October 7-11, 2002, Washington, D. C., eds. R. Noomen, S. Klosko, C. Noll, and M. Pearlman, NASA/CP-2003-212248, pp. 75-86, 2003, available on web site http://cddis.gsfc.nasa.gov/lw13/lw_proceedings.html
- Williams, J.G., Newhall, X X, and Dickey, J.O., "Determination of precession and nutation from lunar laser ranging analysis", paper at IAU Joint Discussion 19 on nutation, in Highlights of Astronomy, Vol. 10, ed. I. Appenzeller, 214-217, 1995.
- Williams, J.G., Newhall, X X, and Dickey, J.O., "Lunar Laser Ranging: Geophysical Results and Reference Frames", Contributions of Space Geodesy in Geodynamics: Crustal Dynamics, AGU Geodynamics Series, V.24, pp. 83-88, Edited by D.E. Smith and D.L. Turcotte, 1993.
- Williams, J.G., Newhall, X X, and Dickey, J.O., "Relativity parameters determined from lunar laser ranging", Phys. Rev. D 53, 6730-6739, 1996.
- Williams, J. G., X X Newhall, and J. O. Dickey, "Lunar Moments, Tides, Orientation, and Coordinate Frames", paper for MORO meeting, June 8-10, 1995 in Pisa, Italy, Planetary and Space Science 44, 1077-1080, 1996.
- Williams, J.G., and Standish, E.M., "Dynamical Reference Franes in the Planetary and Earth-Moon Systems", -JPL Preprint No.169. To be publ. in "Reference Systems", D. Reidel, 1988.
- Williams, J. G., Turyshev, S.G., and Boggs, D.H., Progress in Lunar Laser Ranging Tests of Relativistic Gravity, submitted, 2004.
- Williams, J.G., Turyshev, S.G., Boggs, D.H., and Ratcliff, J.T., Lunar Laser Ranging Science: Gravitational Physics and Lunar Interior and Geodesy, 35th COSPAR Scientific Assembly, July 18-24, 2004, Paris, France, in press in Advances in Space Research, 2005.
- Wilson, P., "Lunar Ranging Modifications for the Laser Ranging System in Wettzell", Fed. Rep. of Germany, Proc. of the 3rd International Workshop on Laser Ranging Instrumentation, Lagonissi, Greece, May 23-27, p.1978.
- Yoshino, T., Schreiber, U., Kawano, N., Kunimori, H., Amagai, J., Tetsuro, Kondo, Takahiro, Iwata, Schlueter, W., and Degnan, J., "Lunar laser ranging by optical transponder collocated with VLBI radio sources on the Moon", Laser Radar Ranging and Atmospheric lidar techniques II, Europto Proc. Vol 3865, pp. 20-26, Florence, Italy, Sept 20-21, 1999.




